T-Kernel 2.0 Extension(T2EX)
T-Kernel 2.0 Extension (T2EX)
●Network Communication
- provides socket interfaces for communication including TCP/IP and UDP/IP
- provides DHCP and DNS client
- provides socket interface API with high degree of compatibility with POSIX specification
- accomplishes resource saving for target embedded devices
○Improvement from POSIX specification
- To avoid excessive abstraction, the API name for socket-related functions has "so_" prefix (to stand for socket).
- If an error occurs, a negative value is returned.
- For the APIs that require timeout, provides APIs that can handle the T-Kernel 2.0 timeout format (TMO, TMO_U) in addition to the APIs of time data format of thePOSIX specification
- Provides so_break() that aborts the ongoing communication forcibly
○Main APIs for network management
- so_socket - Creates an endpoint for communication
- so_accept - Accepts a new connection on a socket
- so_bind - Binds a name to a socket
- so_connect - Connects a socket
- so_listen - Listens for socket connections
- so_select, so_select_ms, so_select_us - Synchronous I/O multiplexing
- so_recvfrom, so_recvmsg - Receives a message from a socket
- so_sendto, so_sendmsg - Sends a message on a socket
- so_gethostname - Gets name of current host
- so_break - Stops socket operation
●File System Support
- supports FAT file system by default
- handles the FAT12, FAT16, and FAT32 file system formats and also uses VFAT long file names
- provides the standard I/O library functions such as fopen() and fprintf()
- provides an API set similar to the file input/output function of the POSIX specification
○Improvement from POSIX specification
- To avoid excessive abstraction, the API name for file-related functions has "fs_" prefix (to stand for file system)
- If an error occurs, a negative value is returned.
- for the APIs that handle timestamps, APIs that can handle the T-Kernel 2.0 time format (SYSTIM, SYSTIM_U) have been provided in addition to the APIs of time data format of the POSIX specification
- supports 64-bit large files
- provides so_break() that aborts the ongoing file operation forcibly
- supports "File System Implementation Part" that is written by users
○Main APIs of file system support
- fs_regist - Registers a file system implementation part
- fs_attach - Connects a file system implementation part
- fs_open - Opens or creates a file
- fs_lseek, fs_lseek64 - Changes the file read/write offset position
- fs_read - Reads from a file
- fs_write - Writes to a file
- s_creat - Creates a file
- fs_truncate, fs_ftruncate, fs_truncate64, fs_ftruncate64 - Truncates or enlarges a file
- fs_sync - Synchronizes the file system
- fs_mkdir - Creates a directory
- fs_break - Stops a file management operation
○File system implementation part
- provides the function for users to independently define program codes that handle a file system
-
useful when special devices and/or special file systems for embedded systems are to be handled
Example 1: FlashROM file system that supports leveling of wearing caused by writing (wear leveling)
Example 2: Latest file systems such as exFAT - manipulation of files through common API from applications
- fs_open(), fs_read(), fs_write(), ...
●Standard C compatible Library
- provides API that is highly compatible with the standard C library (JIS X3010:2003).
○Improvement from the standard C library
- changes the design so that it values the thread-safety because of multi-tasking
- does away with the acquisition of error information by errno, and adopts the method used in T-Kernel.
- eparates the groups of functions that handle the files and the group of functions that handle the sockets.
○Examples of API
-
math.h
log, logf, logl - Natural logarithm function
sin, sinf, sinl - Sine function
sqrt, sqrtf, sqrtl - Square root function -
stdio.h
fprintf, printf, snprintf, sprintf - Formatted output
fscanf, scanf, sscanf - Formatted input conversion
fopen, fopen_eno - Opens file -
string.h
strcmp - Compares two strings
strcpy - Copies a string
●Calendar
- converts from the system time (SYSTIM, SYSTIM_U) of T-Kernel and the time_t numeric time value, to the representation in characters, or in divided elements, and vice versa.
- API name prefix is "dt_" (date/time).
○Improvement from POSIX specification
- If an error occurs, a negative value is returned.
○Main API
- dt_tzset - Sets time zone conversion information
- dt_localtime, dt_localtime_ms, dt_localtime_us - Converts a time value to a broken-down local time
- dt_strftime - Converts date and time to a string
- dt_strptime - date and time conversion
- mktime_eno, mktime - Converts from element-separated local time to calendar time
- gmtime_r_eno, gmtime_r - Converts from calendar time to element-separated UTC time
●Program Load (original feature of T2EX)
- loads a program and then executes it
- API name prefix is "pm_" (program module).
- uses a file or a memory area as a program module
- provides a sample for building a loaded program module.
○Supports two types of load modules
-
a general program ... it executes at the same protection level as the caller
Used when a division of implementation of application is attempted (lib, plug-in, ...) -
a system program . . .it executes at the special privilege level and (and provides the system level I/F).
Enhances OS by providing additional device driver I/F and subsystem I/F.
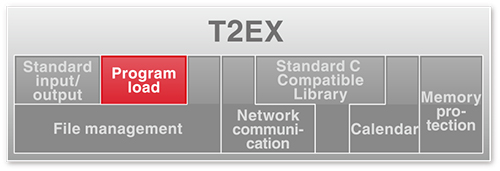
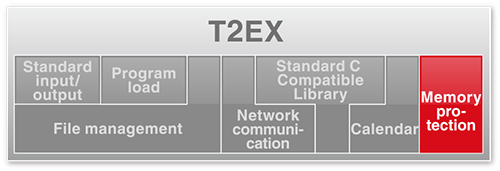
●Memory Protection (original feature of T2EX)
-
provides protection by separation of privilege level and user level
improves the stability and reliability of the entire system by protecting the memory area used by T-Kernel 2.0, T2EX and system programs such as device drivers, etc. from the user application. - provides compact and high-speed memory protection to be used by the small information appliances, etc.
○generates a memory protection violation exception when an illegal memory access is attempted, and executes the exception handling function.
- Exception handling in task: TaskMemFaultHdr()
- Exception handling in task independent part: RawMemFaultHdr()
■Please download T-Kernel 2.0 Extension (T2EX) HERE

 Categories
Categories Supported OS
Supported OS Information
Information
 Download Box
Download Box Latest
Latest




